Sports and gym injuries are not only physically unpleasant, they also cause lethargy and can sometimes even lead to depression.
 Even those who exercise every single day of their lives are prone to workout injuries and knee joint pain. You may have heard how a seasoned sports player can miss matches because of a muscle pull in the gym.
Even those who exercise every single day of their lives are prone to workout injuries and knee joint pain. You may have heard how a seasoned sports player can miss matches because of a muscle pull in the gym.
When gym instructors and trainers tell you that a particular form or posture is not right or bad for your body in the long run then you should avoid them at all costs.
Let’s have a look at some of the common workout injuries: Why do they occur & how to avoid them
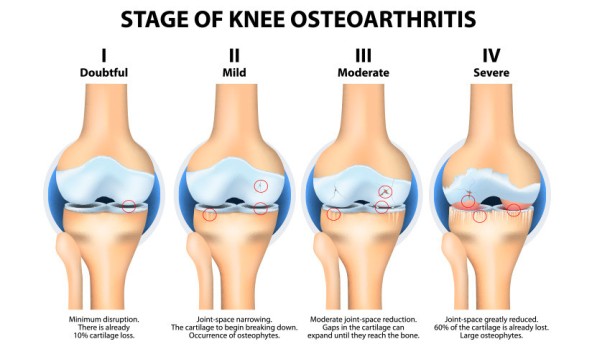
- Knee Injury: Good warm up exercise before workout sessions is something that should compulsorily be a part of your daily gym routine. People, who have just undergone total knee replacement surgery, should not include those exercises that will put too much strain on their knees
- Foot & Ankle Pain: Wearing unsupportive shoes during your cardio workout sessions can lead to foot and ankle pain. There are two major reasons for this: first, you are not giving your foot proper cushioning; and second, the soles of your shoes are not good enough to provide your ankle adequate support.
- Shoulder Injury: Avoid lifting weights that do not match your BMI (Body Mass Index). Your Shoulder Specialist will tell you which sports and activities are good for when you recover from a Shoulder Replacement Surgery.
If you develop a workout injury, follow the “R.I.C.E.” method to keep your injury from getting worse:
R: Rest the injury
I: Ice the injury to lessen swelling, bleeding, and inflammation
C: Apply a compression bandage to minimize swelling
E: Elevate the injury if possible, to reduce swelling
 Let’s Look at the 3 Types of Surgery That Can Be Performed On Your Injured Rotator Cuff:
Let’s Look at the 3 Types of Surgery That Can Be Performed On Your Injured Rotator Cuff: